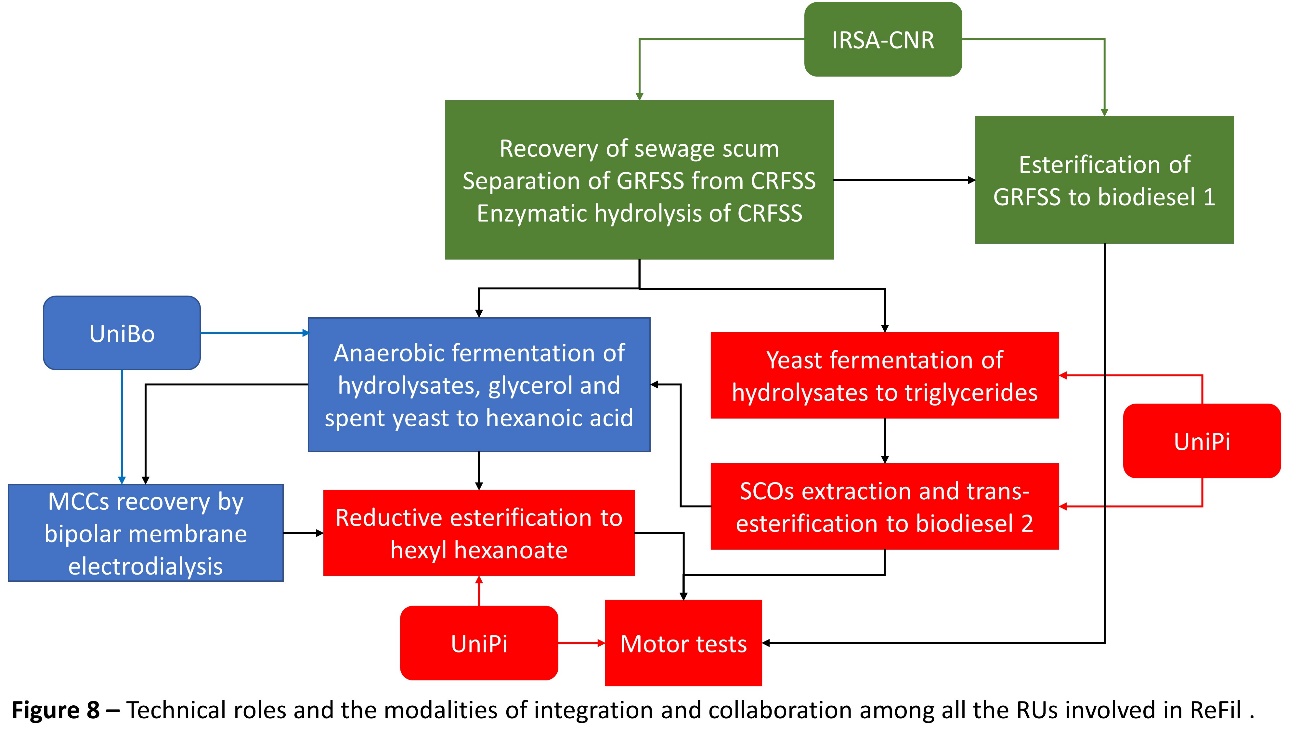
The ReFil project aims to assess the complete valorization of SS separated in conventional WWTPs through the production of new generation biofuels coupled with a near to zero final discharge. To this aim, a multipurpose cascading scheme is proposed to be assessed with laboratory scale experiments. The new biorefinery scheme (Figure 1) includes the production of: (1) FAEEs through direct esterification of naturally occurring lipids in the GRFSS (“Biodiesel 1” in Figure 1) (2) FAEEs through the trans-esterification of newly generated lipids yeast grown on the enzymatically hydrolyzed CRFSS (“Biodiesel 2” in Figure 1) and (3) hexyl-hexanoate (fuel bioadditive) through the catalytic reductive esterification of hexanoic acid (HexAc) previously obtained through anaerobic fermentation of the CRFSS and/or hydrolyzed CRFSS and/or crude glycerol and/or spent yeast.
The obtained biodiesels and the hexyl hexanoate (HexHex) will be tested in bench motor. The alcohol to be used for this study will be the ethanol (instead of the most studied methanol), for evaluating the physico-chemical properties of the relevant products and because it could be potentially obtained from biological routes. In a wider vision, ethanol could be even produced from the hydrolyzed CRFSS, adopting a well-defined route. Besides, considering a maximal valorization approach, the biomethane potential (BMP) of eventual organic leftover (e.g. the obtained at the HexAc separation step) will be assessed as well. In the complex, this project would offer a clear example of application of circular economy principles turning almost totally a waste into resources.
The project will be developed in the following work packages and tasks.